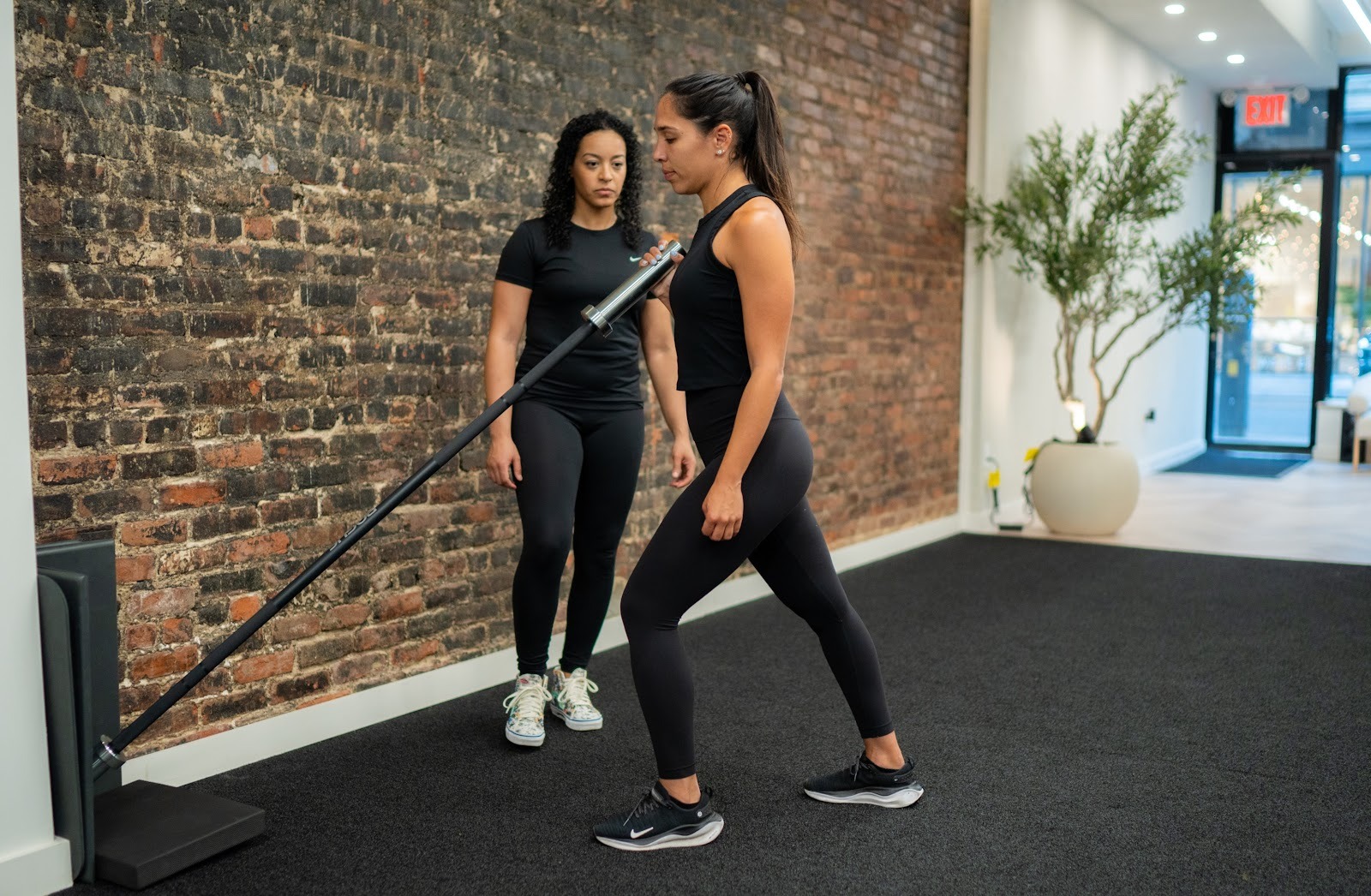
Direct Answer:
Female urinary incontinence treatment depends on the cause but often includes pelvic floor physical therapy, lifestyle changes, bladder training, and medical treatments when necessary. In many cases, strengthening and retraining the pelvic floor muscles can significantly reduce urine leakage and restore bladder control without surgery.
For women, urinary incontinence is more common than many realize—and highly treatable. With the right diagnosis and targeted therapy, most women can improve symptoms and regain confidence in daily activities.
What Is Female Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control, leading to unintentional urine leakage.
This may happen during everyday activities such as:
- Exercising
- Sneezing or coughing
- Laughing
- Lifting heavy objects
- Feeling a sudden urge to urinate
Although often associated with aging, urinary incontinence can affect younger women as well, particularly after pregnancy, intense exercise, pelvic floor strain, or certain medical conditions.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), millions of women experience some form of urinary incontinence during their lifetime.
The good news: most cases improve significantly with non-invasive treatments, especially pelvic floor rehabilitation.
Common Types of Urinary Incontinence in Women
Different types of incontinence require different treatment approaches.
Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence occurs when physical pressure on the bladder causes leakage.
Common triggers include:
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Jumping
- Running
- Heavy lifting
- Laughing
This often happens when the pelvic floor muscles weaken and cannot properly support the bladder and urethra.
Stress incontinence is especially common after:
- Pregnancy
- Childbirth
- High-impact sports
- Chronic coughing
Urge Incontinence (Overactive Bladder)
Urge incontinence involves a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by leakage.
Women may feel like they must rush to the bathroom immediately.
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Waking up at night to urinate
- Sudden urgency
- Inability to hold urine
This type of incontinence is often related to overactive bladder muscles or nerve signaling issues.
Mixed Incontinence
Mixed incontinence is a combination of:
- Stress incontinence
- Urge incontinence
For example, a woman may leak when exercising but also feel sudden urinary urgency.
Treatment usually combines pelvic floor therapy, bladder training, and lifestyle changes.
Overflow Incontinence
Overflow incontinence happens when the bladder cannot empty completely, causing frequent dribbling.
Possible causes include:
- Nerve problems
- Bladder obstruction
- Certain medications
Why Do Women Experience Urinary Incontinence?

Several factors can contribute to bladder control problems.
Pregnancy and Childbirth
Pregnancy places pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, which support the bladder.
Vaginal delivery can stretch or weaken these muscles, sometimes affecting bladder control.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Weakness
The pelvic floor acts like a support hammock for the bladder, uterus, and bowel.
When these muscles weaken, the bladder may lose support, causing urine leakage during physical activities.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations—especially after childbirth or during perimenopause—can affect bladder tissue and pelvic floor strength.
High-Impact Exercise
Athletes and active women sometimes develop exercise-related urinary leakage.
Activities that increase abdominal pressure include:
- Running
- CrossFit
- Weightlifting
- Jump training
Chronic Constipation
Constipation increases pressure in the abdomen, which can strain the pelvic floor muscles over time.
Symptoms That May Require Evaluation
Occasional leakage can happen. However, persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Frequent urine leakage
- Sudden strong urges to urinate
- Pain during urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Blood in urine
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
A proper evaluation can identify the underlying cause of incontinence and guide treatment.
Female Urinary Incontinence Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and severity of symptoms. Most women begin with conservative treatments, which are highly effective.
1. Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Pelvic floor physical therapy is one of the most effective first-line treatments for urinary incontinence.
A pelvic health physical therapist evaluates:
- Pelvic floor muscle strength
- Muscle coordination
- Breathing mechanics
- Core stability
- Bladder habits
From this assessment, a personalized treatment plan is created.
Benefits of Pelvic Floor Therapy
Pelvic floor rehabilitation can help:
- Strengthen bladder support muscles
- Improve bladder control
- Reduce urine leakage
- Improve coordination between muscles and nerves
- Restore confidence during exercise and daily activities
Research published in the International Urogynecology Journal shows pelvic floor muscle training significantly improves urinary incontinence symptoms.
2. Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels)
Kegel exercises strengthen the muscles that control urination.
These exercises involve contracting and relaxing pelvic floor muscles repeatedly.
Benefits include:
- Stronger bladder support
- Improved urinary control
- Reduced leakage during activity
However, many women perform Kegels incorrectly. This is why guided therapy often produces better results.
3. Bladder Training
Bladder training teaches the bladder to hold urine longer.
This method involves:
- Scheduled bathroom visits
- Gradually increasing the time between urination
- Learning to delay urges safely
Over time, bladder capacity improves.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Simple lifestyle adjustments can reduce bladder irritation and leakage.
Helpful strategies include:
Limiting Bladder Irritants
Common irritants include:
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Carbonated drinks
- Artificial sweeteners
- Spicy foods
Managing Fluid Intake
Drinking adequate water helps prevent bladder irritation while avoiding excessive intake.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight increases pressure on the bladder.
5. Medical Treatments
If conservative therapies are not enough, medical treatments may be recommended.
Possible options include:
- Medications for an overactive bladder
- Vaginal pessaries to support pelvic organs
- Botox injections to calm bladder muscles
- Nerve stimulation therapy
These treatments are typically recommended after pelvic floor therapy and lifestyle changes.
6. Surgical Treatments
Surgery is usually reserved for severe cases.
Common procedures include:
- Mid-urethral sling surgery to support the urethra
- Bladder neck suspension to improve bladder support
Surgical options are generally considered only when other treatments have not worked.
How Pelvic Floor Therapy Helps Women Regain Bladder Control
Pelvic floor therapy is becoming a cornerstone of urinary incontinence treatment.
Treatment often includes:
Muscle Retraining
Targeted exercises strengthen the pelvic floor and improve bladder support.
Biofeedback Therapy
Biofeedback uses sensors to help women understand how their pelvic floor muscles work.
This helps patients:
- Contract muscles correctly
- Relax muscles when needed
- Improve coordination
Breathing and Core Training
The diaphragm, core muscles, and pelvic floor work together.
Proper breathing patterns help regulate pressure inside the abdomen and improve bladder control.
Behavioral Strategies
Therapists teach practical habits such as:
- Optimal bathroom posture
- Relaxation techniques
- Bladder training strategies
Real-World Impact: Why Treatment Matters
Urinary incontinence affects more than physical health.
It can impact:
- Exercise confidence
- Work productivity
- Social activities
- Mental health
However, many women delay treatment due to embarrassment.
Studies show up to 50% of women with incontinence never seek medical help, even though effective treatments exist.
Early intervention can dramatically improve outcomes.
How Pelvis NYC Helps Women with Urinary Incontinence

At Pelvis NYC, we specialize in pelvic floor physical therapy designed to treat urinary incontinence and other pelvic health conditions.
Our approach includes:
- Comprehensive pelvic floor assessments
- Evidence-based pelvic floor therapy
- Biofeedback training
- Core and breathing coordination
- Lifestyle and bladder habit coaching
We understand that bladder control issues can feel frustrating or embarrassing. Our goal is to provide private, supportive, and effective care to help you regain confidence in your body.
👉 If you’re experiencing urinary leakage or bladder urgency, Pelvis NYC can help. Schedule a consultation today and take the first step toward better bladder control.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best treatment for female urinary incontinence?
Pelvic floor physical therapy is often the most effective first-line treatment. Strengthening and retraining pelvic floor muscles can significantly reduce leakage in many women.
Can urinary incontinence go away on its own?
Mild cases may improve with lifestyle changes and pelvic floor exercises. However, persistent symptoms often require guided treatment.
How long does pelvic floor therapy take to work?
Many women notice improvement within 6–12 weeks of consistent therapy and exercises.
Is urinary incontinence normal after pregnancy?
Yes, many women experience temporary bladder leakage after childbirth due to pelvic floor strain. Pelvic floor therapy can help restore strength and control.
When should I see a doctor for urinary incontinence?
Seek medical evaluation if leakage is frequent, worsening, painful, or affecting your quality of life.
Key Takeaway in Female Urinary Incont
Female urinary incontinence is common, treatable, and often reversible.
Effective treatment options include:
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- Bladder training
- Lifestyle adjustments
- Medical treatments when needed
For many women, pelvic floor rehabilitation provides the most effective non-invasive solution, restoring bladder control and improving quality of life.